A new world order? BRICS nations offer alternative to West
Predictions about the BRICS countries as the fastest growing economies haven’t quite panned out. Instead, the alliance is now offering a diplomatic forum and development financing, outside of the Western mainstream.
The acronym began as a somewhat optimistic term to describe what were the world’s fastest-growing economies at the time. But now the BRICS nations — Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa — are setting themselves up as an alternative to existing international financial and political forums.
“The founding myth of the emerging economies has faded,” confirmed Günther Maihold, deputy director of the German Institute for International and Security Affairs, or SWP. “The BRICS countries are experiencing their geopolitical moment.”
Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa are trying to position themselves as representatives of the Global South, providing “an alternative model to the G7.”
The G7 is an “informal forum” of heads of state of the world’s most advanced economies, founded in 1975. Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, Japan, Canada and the US are members, as is the EU.
The acronym BRIC, which initially stood for Brazil, Russia, India and China, was coined by Jim O’Neill in 2001 when he was chief economist of the multinational investment bank, Goldman Sachs. At the time, the four countries had sustained rates of high economic growth and the BRIC label stood for economic optimism about the future of those nations. Opponents of the label said the countries were too diverse to be grouped together like this and that it was really just a Goldman Sachs marketing ploy.
But what may have started as a marketing ploy to encourage investors has grown into a platform for intergovernmental cooperation similar to the G7. In 2009, the four nations met for their first summit in Russia’s Yekaterinburg. In 2010, South Africa was invited to join the group, adding the “S” to BRICS.
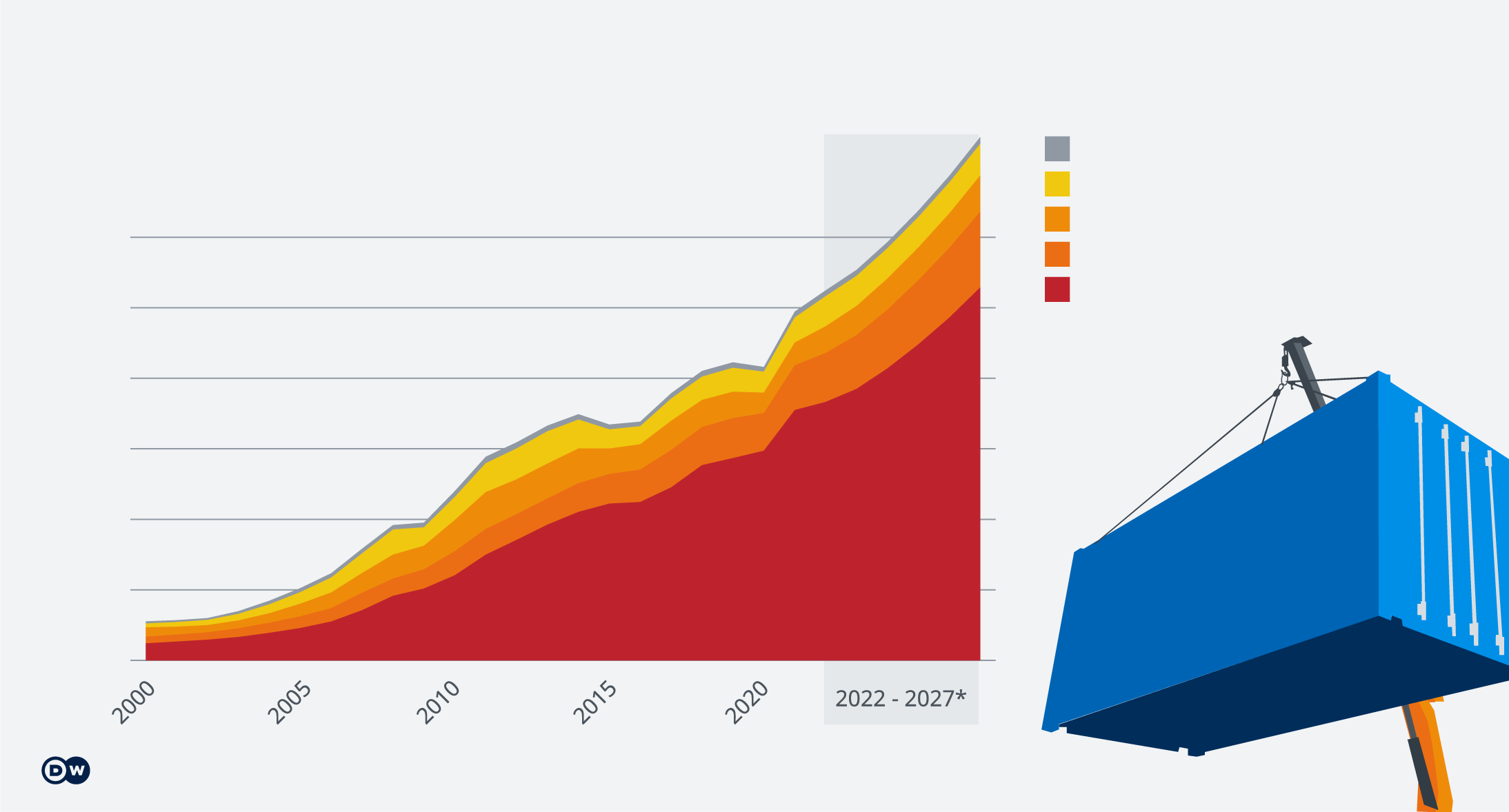
Challenging the World Bank model
In 2014, with $50 billion (around €46 billion) in seed money, the BRICS nations launched the New Development Bank as an alternative to the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund. In addition, they created a liquidity mechanism called the Contingent Reserve Arrangement to support members struggling with payments.
These offers were not only attractive to the BRICS nations themselves, but also to many other developing and emerging economies that had had painful experiences with the IMF’s structural adjustment programs and austerity measures. This is why many countries said they might be interested in joining the BRICS group.
The BRICS bank is open to new members. In 2021, Egypt, the United Arab Emirates, Uruguay and Bangladesh took up shares. However, these were much lower than the respective $10 billion investments made by the bank’s founding members.
Set to expand
South African Foreign Minister Naledi Pandor has said worldwide interest in the BRICS group was “huge.” In early March, she told television interviewers that she had 12 letters from interested countries on her desk.
“Saudi Arabia is one,” she said. “United Arab Emirates, Egypt, Algeria, and Argentina,” as well as Mexico and Nigeria.

